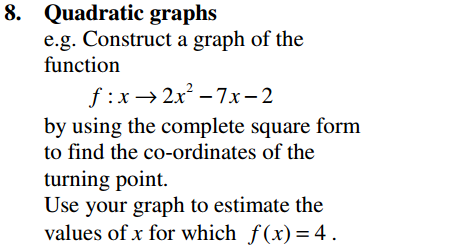
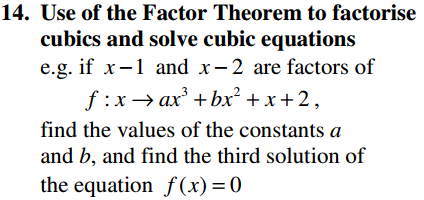
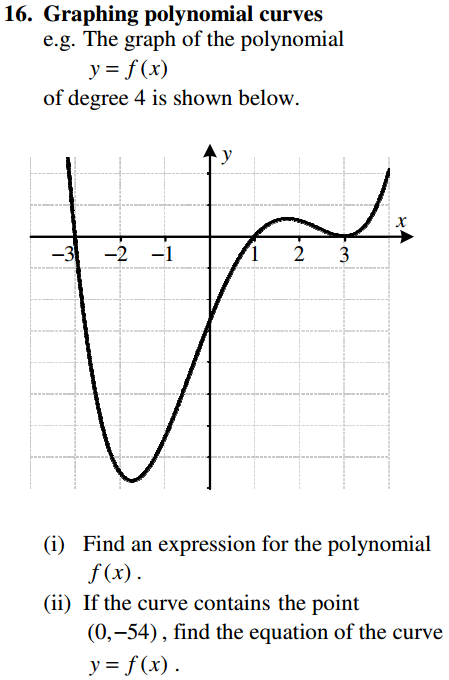
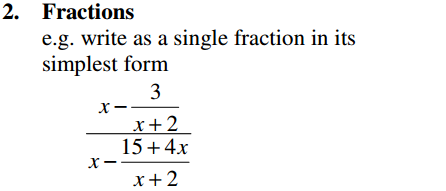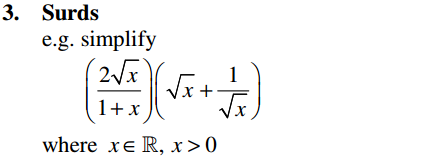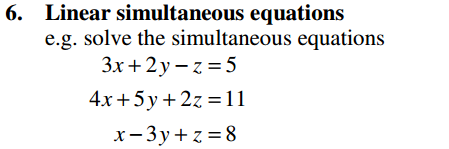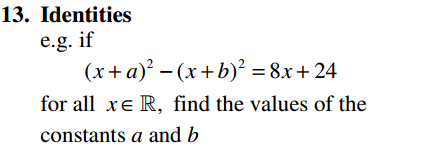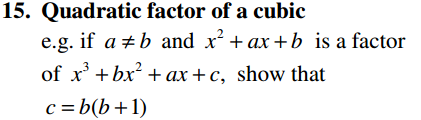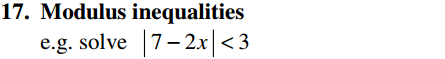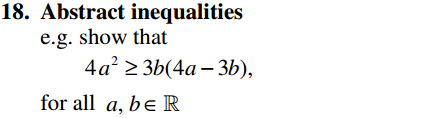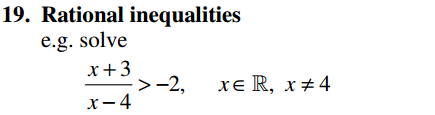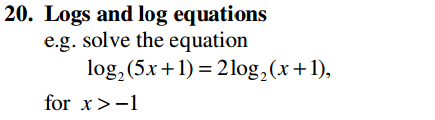Algebra Overview
|
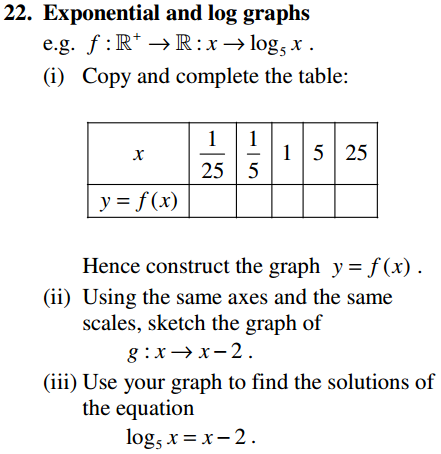
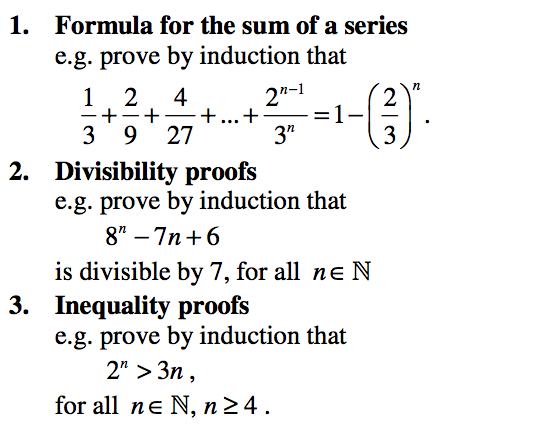
For a reasonably comprehensive revision of Algebra this page contains 3 Printable Worksheets with solutions.
|
22 Revision Questions |
4 Revision Questions |
4. Prove de Moivre's Theorem using induction
|