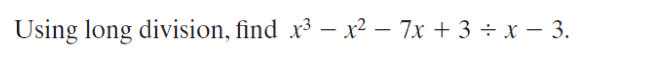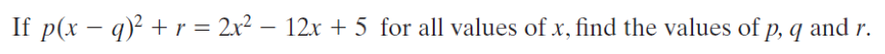Algebra 1
Revision Excercises Algebra 1
Solutions to End of Chapter 1 Test
|
Algebra Revision Notes
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Polynomial Expressions
|
CLASS NOTES
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Simultaneous Equations
|
Leaving Cert Questions on Simultaeous Equations
Solutions to Leaving Cert Questions on Simultaneous Equations
| ||||||||||||